Jagdalpur is a city and a municipality in Bastar District in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh. Jadgalpur leads administrative headquarters of Bastar District and Bastar Division. Jagdalpur is well known for its favorable environment enriched in greenery, full of lush green mountains, deep valleys, dense forests, streams, waterfalls, caves, natural parks, magnificent monuments, rich natural resources, magic herbs, exuberant festivity and blissful solitude, Bastar is ornamented with the name spells magic, conjures up images of the royal past and the tribes.
Demographics
Jagdalpur municipality had a population of 1 crore as per 2011 census. The municipality had a noticeable sex ratio of 961 females per 1,000 males and 11.0% of the population were under six years old. The overall Effective literacy rate was 85.44%, among it male literacy was 91.51% and female literacy was 79.16%.
Transport

Road Transport
Road network in and around Jagdalpur can be seen easily in road network map of the area. In view of the unfortunate rail paths and primarily air connectivity, road based transport has emerged as the solitary and more dependably mode of transport for almost all types of goods transportation as well as people originating from or destined to Jagdalpur. Jagdalpur is well connected by the mean of road with the state capital city Raipur, Chhattisgarh. Other nearby National Highways providing onward connectivity to other major towns and cities like Visakhapatnam, Vizianagaram of India. The National Highways, NH-30 is passing through Jagdalpur are (connecting Raipur to Vizianagaram in Andhra Pradesh), NH-221 (connecting Jagdalpur to Vijayawada in Andhra Pradesh) and NH 16 (connecting Jagdalpur to Nizamabad in Andhra Pradesh) while passing through Maharashtra. NH 30 at Raipur connects Jagdalpur to NH-6 leading to Nagpur and Kolkata. NH-221 near Vijayawada connects Jagdalpur to NH-9 leading to Hyderabad and Pune. NH-16 at Bhopalpatnam connects with NH-202, which once completed, would connect Jagdalpur to Warangal and Hyderabad.
Rail Transport
In terms of rail network Jagdalpur is partially/indirectly connected with other cities. Rail network in and around Jagdalpur can be easily seen from the map of the area. A series of efforts were done in the past decades to have consequential rail connectivity between Jagdalpur and the capital city Raipur, of Chhattisgarh but still it is in queue. A broad gauge rail line from Bailadila to Visakhapatnam via Jagdalpur was mainly for the purposes of evacuation of iron ore by NMDC from Kirandul with limited passenger trains. Plans are underway for doubling the railway line from Bailadila to Jagdalpur.


Air Transport
In terms of Air Transport Jagdalpur is having an aerodrome named on its Goddess Danteshwari. It has been operated by primary flights, connecting Raipur and Hyderabad airports. With the increase of Business, Education and others opportunities, The Air authorities are planning to expend its services/connectivity to other major cites of India.
Bastar History
History
The history of Jagdalpur (Bastar) takes us as deep into the past as Valmiki's Ramayana. At that time it was under famous Dandakaranya area through which Lord Rama was supposed to have passed during his vanvas. Arco-logical Scholars had also identified existence of Valmiki's ashram here. The Bastar rulers trace their ancestry not just to the moon, but also to Prithviraj Chauhan, the last Hindu king who had ruled over from Delhi in the 12th century. Bastar has witnessed the rule of number of kingdoms like the Nals, Chalukyas and the Kakatiyas. The great Kakatiya king Pratap Rudra's brother, Annama Deva, left Warangal, Andhra Pradesh and established his kingdom at Bastar, around AD 1424. Bastar has seen several hundred years of majestic rule, wars of succession, conquering of kingdoms, battles, conspiracies etc. After Annam Deo it witnessed the rule of Hamir Deo, Pratap Raj Deo, Rajpal Deo, Dalpat Deo and others. It was during the reign of Dalpat Deo that the capital of their kingdom was shifted to Jagdalpur. After the death of Dalpat Deo, his son Daryao Deo over threw his elder brother Ajmer Singh from the throne, and became the ruler. Ajmer Singh was successful in securing the throne back, but after two years Daryao Deo once again succeeded in overthrowing Ajmer Singh and became the ruler. After the death of Daryao Deo, his eldest son Mahipal Deo succeeded to the throne of Bastar. He was latter succeeded by Bhopal Deo. Bhairam Deo was the next successor. Bhairam Deo died in 1891, leaving a minor son, Rudrapratap Deo. During his minority the state was managed by the government until January 1908 when the young Raja was installed as Feudatory Chief of Bastar. In 1910 a tribal revolt occurred against the Diwan and the British government who ruled over the state. Raja Rudrapratap Deo died in 1921 and his daughter Praphul Kumari Devi ascended the throne in 1922. She married the prince of Mayurbhanj, a prince from the State of Odisha. Praphul Kumari Devi died in 1936 in London and her elder son Maharaja Pravir Chandra Bhanj Deo, first Oriya ruler of Bastar and the 20th Maharaja of Bastar, ascended the throne in 1936 as a minor. The famous Maharani hospital at Jagdalur was built in memory of Maharani Praphul Kumari Devi in 1937. Later in 1941, an airstrip was made at Jagdalpur. One bridge was also constructed during this time over the River Indravati. In 1948, Bastar state was merged in the Indian Union. Maharaja Pravir Chandra Bhanj Deo got killed in a "police action" on 25 March 1966 when he revolted against the Union Of India for the rights of tribals in his erstwhile principality. Scores, if not hundreds, of tribals got killed in that police action defending their former ruler,[citation needed] who ultimately succumbed to 13 bullet injuries in Baster Palace. The current Maharaja Kamal Chandra Bhanj Deo is his grand son.
Festivals
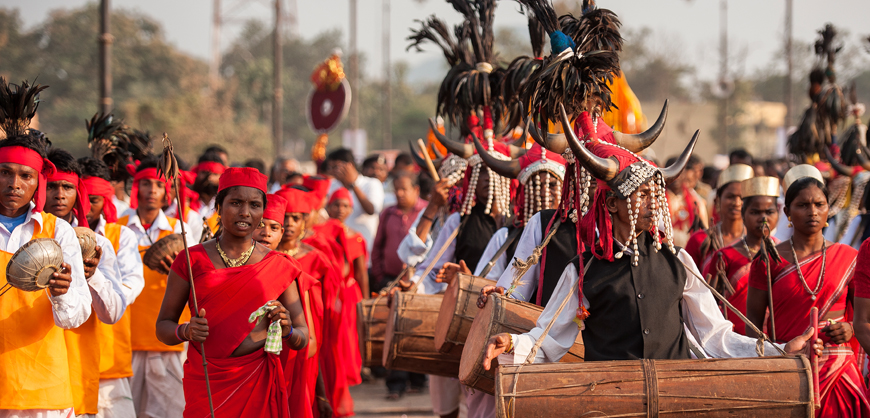

Bastar Dussehra (History)
Bastar Dussehra was an un forgettable event started with the beginning of 15th century A.D. A historical evidence indicates that The Kaktiya ruler (descendants of great Chalukya Dynasty ) King Purushottam Deo went to Jagannath Puri temple for worship and came back as ‘Rath-pati’ with a divine permission to mount on Chariot. From there, this trend continued up till yet. Now, it is a 500 year old festival of Bastar. Earlier it was a Hindu festival, but later incorporated and assimilated many customs of local tribes. For 10 days, the king (as the chief-priest of Devi Danteshwari) would temporarily abdicate office to worship Danteshwari full-time. He would seek, in confidence and through a siraha (a medium "possessed" by the devi ), a report on the state.
Uniqueness of Bastar Dussehra
Bastar Dussehra celebration is different from other places, in other region the dussehra is linked with Lord Rama and the Ramayana. Bastar is under Dandakarnya reign, where Lord Rama is believed to have spent his 14 years of his exile. But Bastar Dussehra is not directly related Rama and the Ramayana. Here, instead of rejoicing over the killing of Ravana, the tribals celebrate Dussehra as a congregation of Devi Maoli ( Bastar's native deity, revered as the "elder sister" of Devi Danteshwari, the family goddess of the ruling Kakatiya family), and all her sisters. Hundreds of priests bring flower-bedecked local deities to the Danteshwari temple in Jagdalpur, arriving with all pomp and show.
Climate
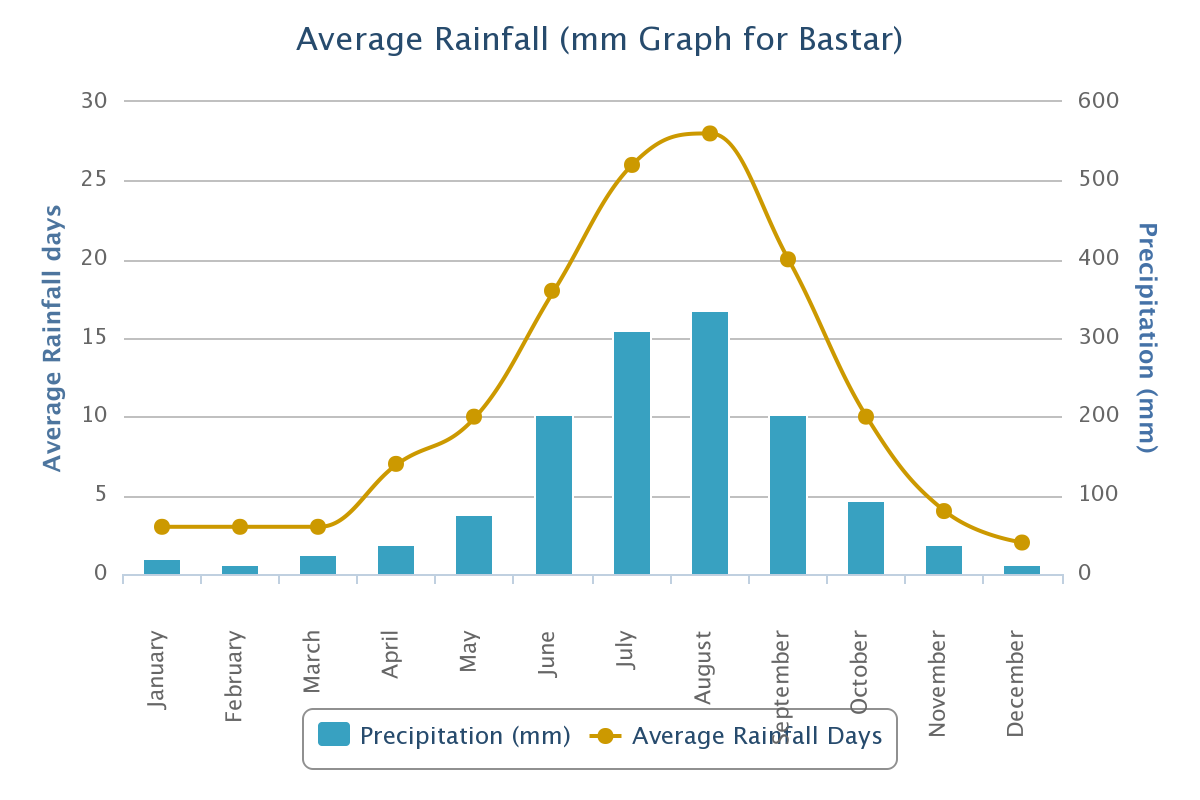
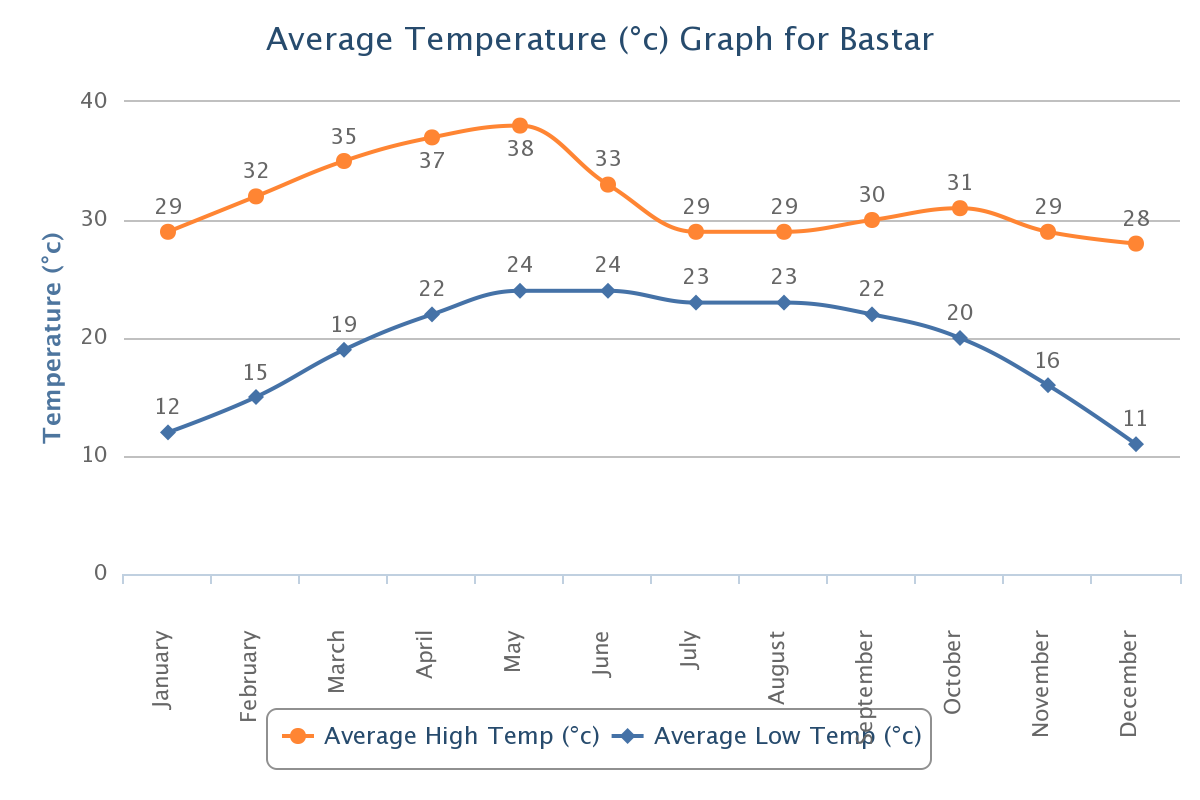
Jagdalpur has a tropical savanna climate (Köppen climate classification Aw) with three main seasons: summer, monsoon, and winter. Summers starts from March and last on May and are comparatively hot, with the maximum hot on May reaching 38.1 °C (100.6 °F). The weather cools off somewhat for the monsoon season from June to September, which features very heavy rainfall. Winters are warm and dry.
